What is Network Latency? How Managed Services Helped in To Avoid Delays In Bandwidth?
In terms of Networking, Latency Means Delay in serving. Network latency has a significant impact on the end-user experience. Actually, a network’s latency is the manner by which long it takes to send information starting with one point on it then onto the next. So the lower a network’s latency, the quicker it is. Ventures can utilize instruments like network execution screens (NPMs) to inspect all that influences their network’s exhibition. One angle that decides how well your network is performing is latency.
Network latency depicts delays in information transmissions that happen on a network. While latency ordinarily eludes to the time period a framework or work process takes to finish, network latency envelops any postponement in information sent starting with one piece of the network then onto the next. It can here and there be difficult to keep away from totally, yet organizations should create an endeavor to eliminate as much latency as possible. Peruse on to find how your venture can diminish network latency and lift your network’s productivity.
How Managed Services Can Avoid Delays in Bandwidth?
The liberation of the media communications industry in the course of recent years has expanded the trouble of introducing the broad cabling required by present day organizations. This issue fundamentally results from disarray over which gathering has obligation regarding conveying a specific broadcast communications administration to a given office. This complexity increases the value of a Managed Service Provider (MSP) who specializes in providing onsite technology services to achieve a reliable deployment.
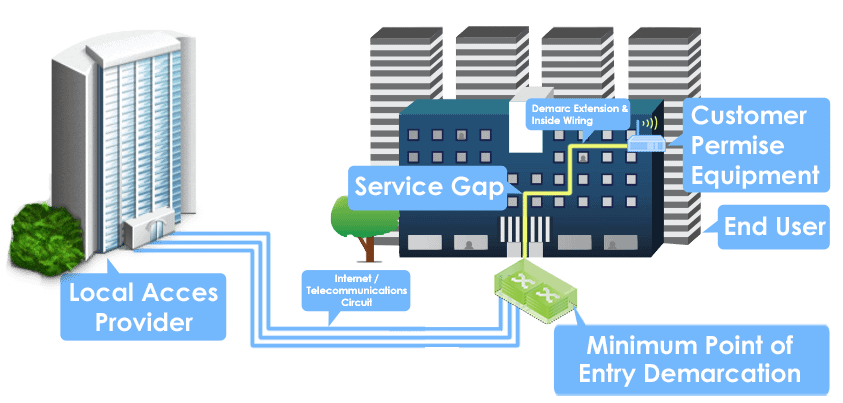
Demarc Extension Defined: A demarcation extension, commonly known as a demarc extension, is the transmission path for a telecommunications circuit that originates from the Local Exchange Carriers (LEC’s) interface and ends at the termination point before the Customer Premises Equipment’s (CPE’s) interface.
MPOE: A facility’s demarc point is often called the minimum point of entry (MPOE) to emphasize the fact that it should occur as soon as possible after entering the facility. A circuit is typically delivered to the MPOE, which should be the closest point at which it is practical to deliver the circuit after the cable enters a building or the point at which the cabling crosses the property line.
In addition to the technology expertise, an MSP typically provides certified project management skills to manage stakeholders in the supply chain. The supply chain of a telecommunications circuit routinely involves multiple stakeholders, making it important to distinguish their specific roles, which are as follows:
Number of factors affects a network’s latency, including:
Connection type – The kind of association affects its speed. Link and fibre associations for the most part have exceptionally low latency (great) while copper has a marginally higher latency (not very great). A satellite connection would have a higher latency still.
Distance – The further you are away from the server holding the content you need, the more extended the information needs to travel, and the additional time it will take to arrive at your PC. Therefore greater distances mean greater latency.
Congestion – A clogged network conveying a lot of information needs to put content in a line and convey it in arrangement. So your data has to wait its turn, meaning high latency again.
Efficiency – A productive network measures the information it gets rapidly at every hub, determining its destination and moves it on with minimum processing delay.
What causes network latency?
There are several potential causes of network latency, and not every one will increase delays on your enterprise’s network. Utilizing NPMs and different instruments, undertakings can sort out explicit components that influence their presentation, including those that expansion (or reduction) latency. Some of the most common causes of latency include:
Device CPU overload
Network devices require CPU power in order to send and receive transmissions. If the node currently doesn’t have enough CPU power available, it will be slow to fully process data heading through it.
Network bottlenecks
Bottlenecks on your network create congestion which reduces the amount of time it takes for data to travel through it. On the off chance that your information is compelled to head out through a bottleneck to arrive at its objective, it will definitely be postponed.
Packet analysis
Nodes on your network, such as routers, need to analyse any packets that are sent to it before it sends them further along the network. On the off chance that a switch isn’t appropriately designed, it may postpone the transmission.
How can you reduce network latency?
Latency affects every enterprise and it isn’t possible to fully prevent it. However, your enterprise can proactively reduce the amount of network latency in your infrastructure
Quality of service
Quality of service provisions available network resources to prioritize bandwidth for critical data transfers. In the event that you have a cycle or application that requires a great deal of data transfer capacity, nature of administration conventions will save the essential assets until they’re required.
Network routing protocols
Your network needs to be able to route out pathways that data can take on your network. This is significant not just for knowing the foundation of your network, but also to help avoid slow performing areas.
Wi-Fi latency inconsistencies
Wi-Fi networks can have extremely inconsistent latency times, as signal strength and interference can slow down data transfers. At whatever point conceivable, you should plan your WiFi network to maintain a strategic distance from obstruction and spot passageways in smart areas that give greatest inclusion.